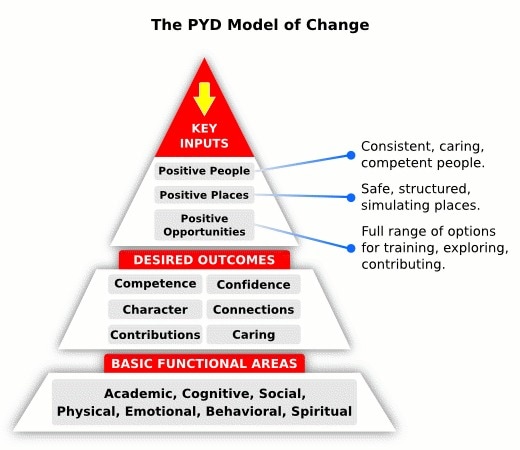
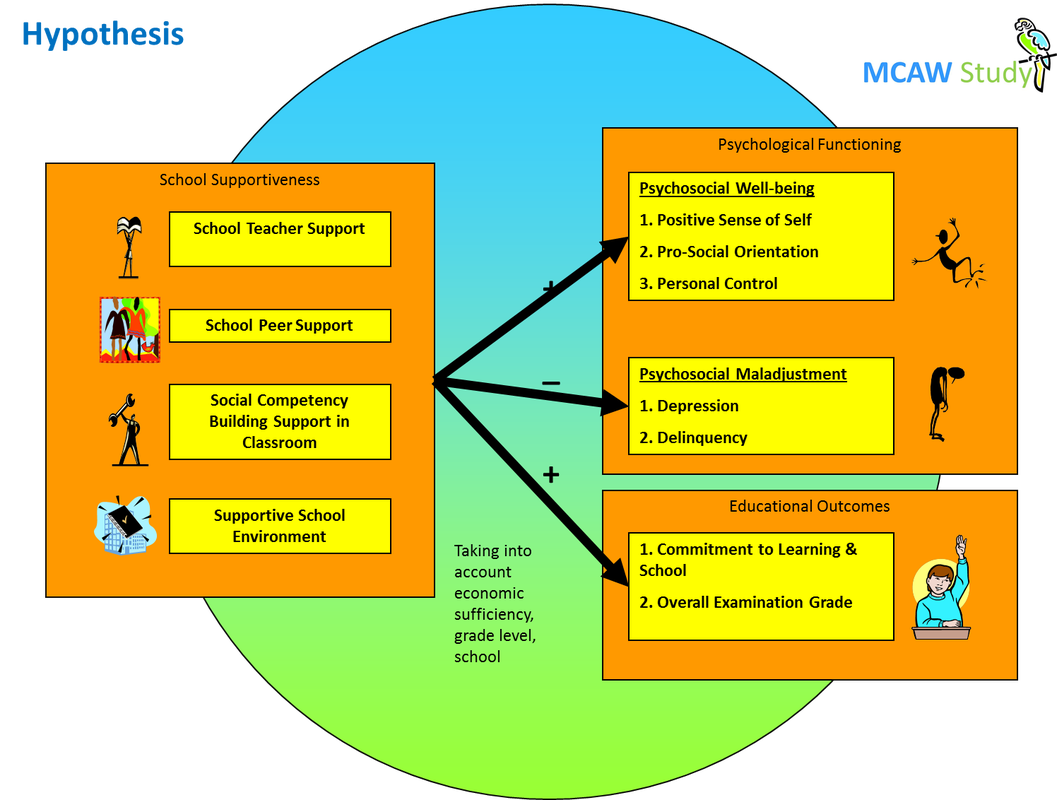
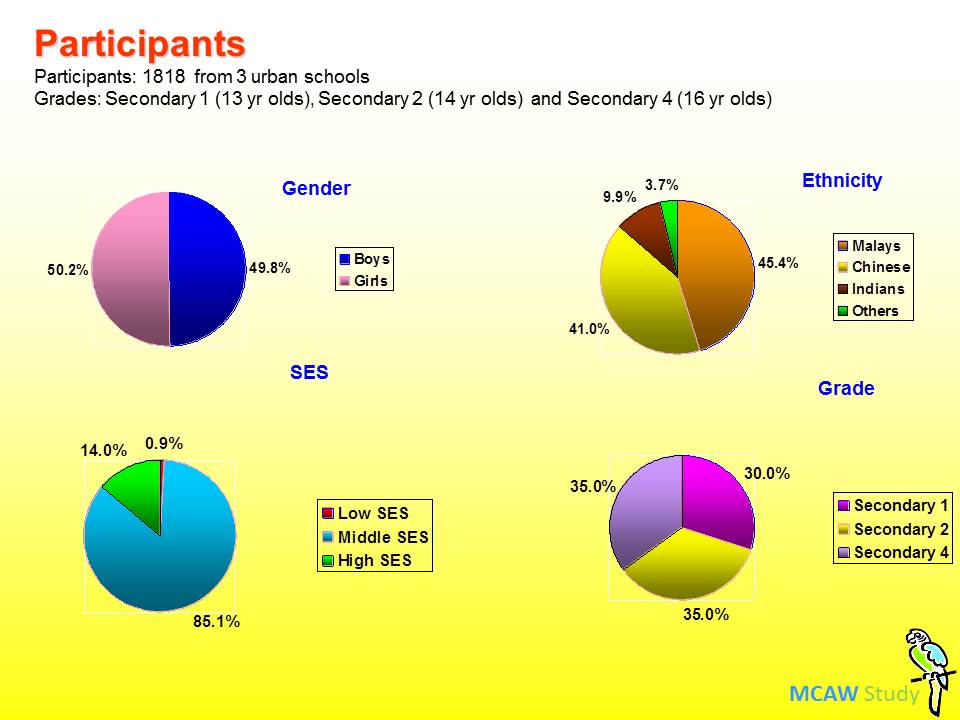
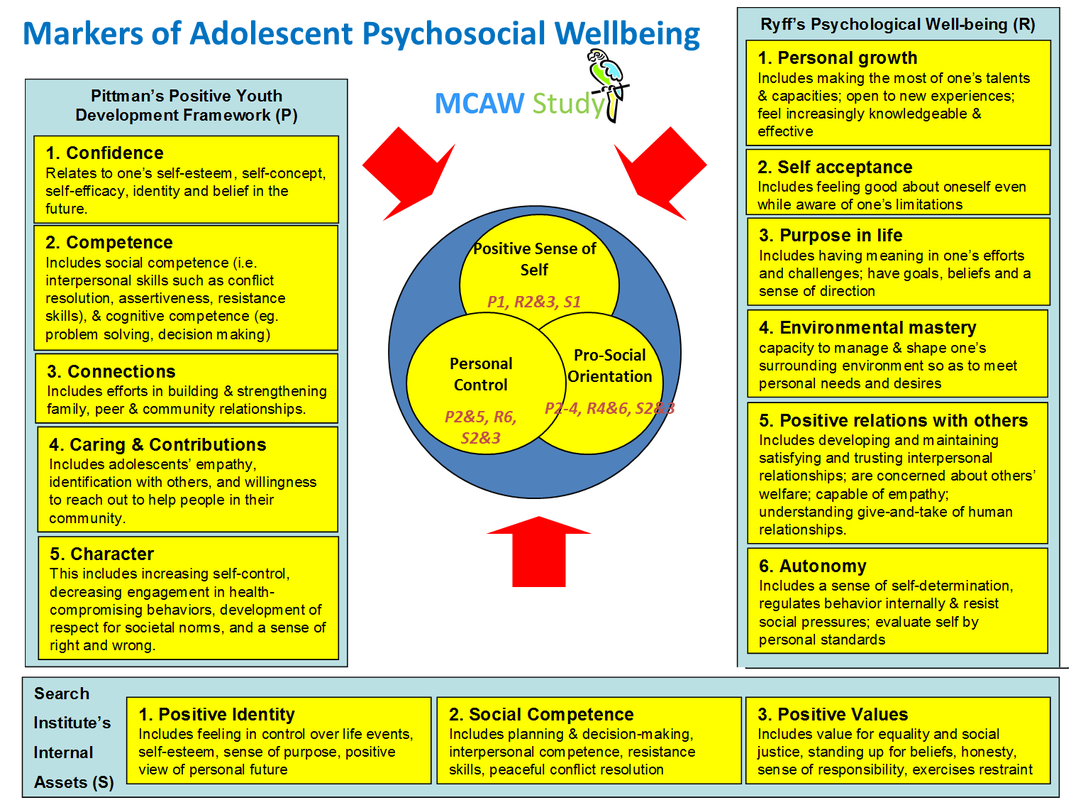
The Malaysian Child & Adolescent Wellbeing (MCAW) Study
References are inserted as links in the text below. Blue hyperlinks will take you to journal articles, videos, news reports or additional information about this study.
The Critical Contribution & Relevance for 2018 & Beyond
|
Reports over the past 15 years show increase in psycho-social distress among youth in Malaysia.
At the same time we observe increase in youth problems in schools and the workplace. MCAW has two key contributions: 1. In promoting the inclusion of psycho-social well-being as a measure of youth development in the country (that is distinct from and more than merely measuring psycho-social distress). 2. In pursuing the likelihood of how social supportiveness in schools can increase psycho-social well-being and reduce psycho-social distress. This study builds on my experience and prior work on large-scale studies in Communities That Care across close to 100 communities in Pennsylvania. It feeds my passion in addressing issues of depression and suicide in young people, and in showing how specific support and developmental assets can promote Positive Youth Development. Much of the work here has been used in applied research, particularly in our launching of Mentoring Malaysia that was funded by UNICEF (co-developed by Gomez & Ang, 2006). Grant FundingMCAW was supported by the United States Fulbright Program, The Prevention Research Center at Penn State, and two grants I received from Jacobs Foundation and Search Institute.
|
|
The Big Picture
This presentation will focus on School Supportiveness and Psycho-social Well-being.
Introduction
A basic psychological need of adolescents is for supportive relationships with adults and peers (Erickson, 1968). Child development researchers and sociologists both emphasize the value of strong supportive social relationships (e.g., attachment and friendships) to family, peers and the community that provide caring, empathy, and social problem-solving skills (Moore, Evans, Brooks-Gunn, & Roth, 2001). There is a positive relationship between social support and psychological well-being in adolescents (Rosenfeld et al., 1998). Broad-based social support is seen as contributing to adjustment and development, and is a powerful buffer and protective factor in resilient children and adolescents, both in western societies and in Asian adolescents (Clark, 1991; Coie et. al., 1993; Richman & Bowen, 1997; Takakura & Sakihara, 2001).
Markers of Adolescent Psychosocial Wellbeing
Positive Sense of Self
|
Prosocial Orientation
|
Personal Control
|
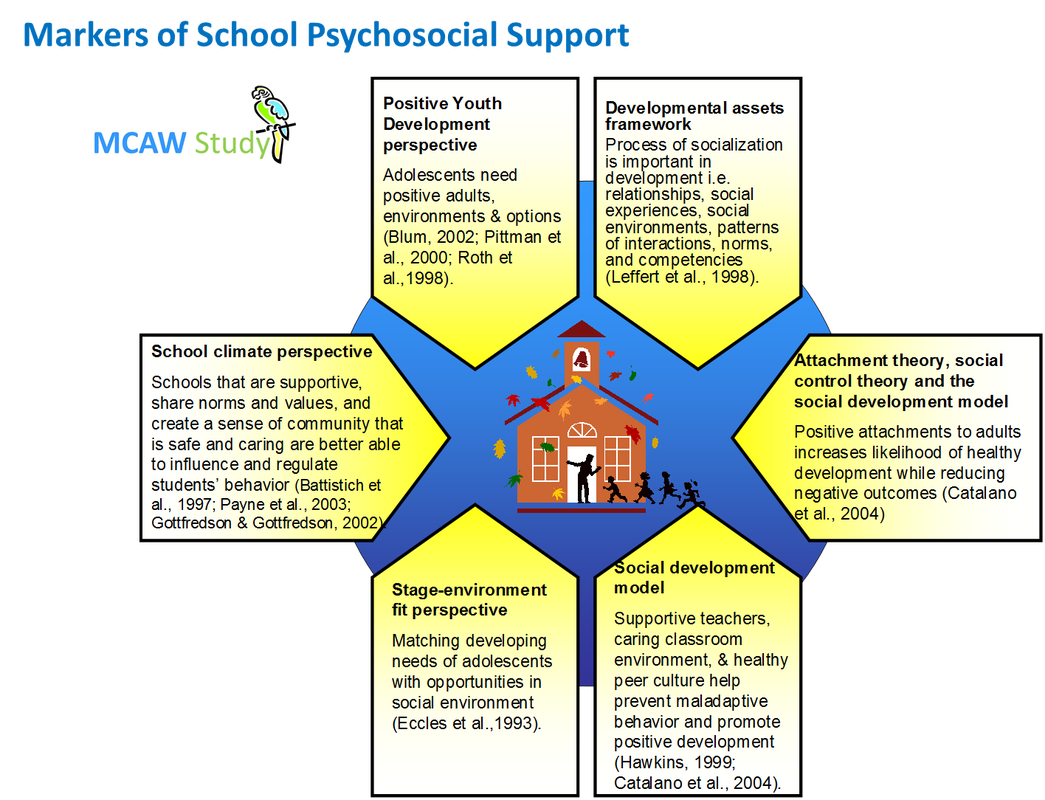
Markers of School Psychosocial Support
School Teacher
|
School Peer
|
Social Competency Building Support
|
Supportive School Environment
|
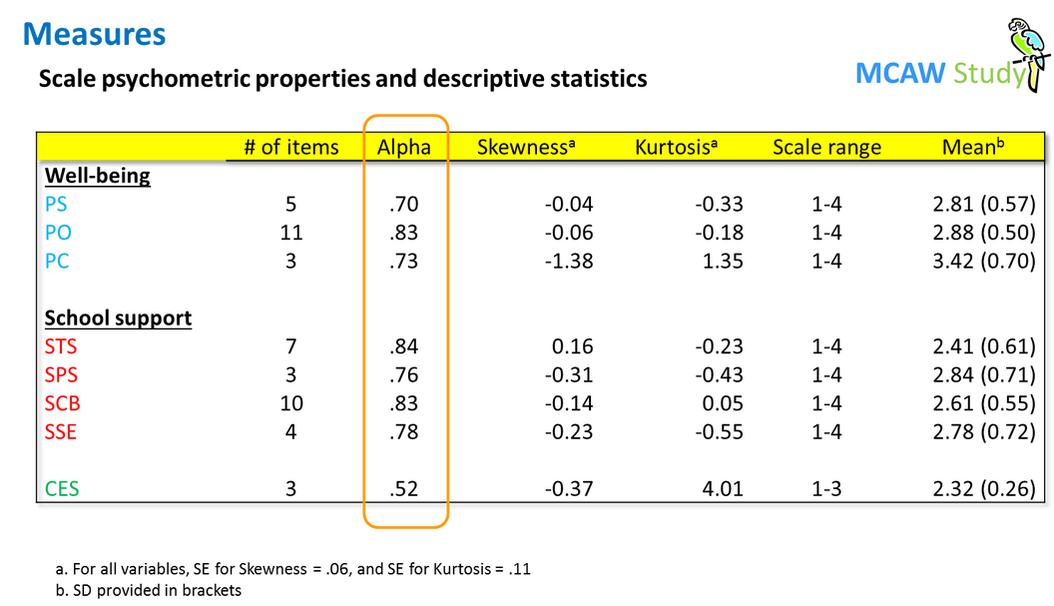
A paper-and-pencil self-report instrument was developed for classroom administration. Items were first translated into Malay (the primary medium of instruction in Malaysian schools) by the investigators who are bi-lingual. Most items had response options ranging from 1 = Not at all or Rarely, to 4 = Extremely or Almost Always.
Want to take a peek at the survey, contact us at ARCCADE @ Gmail . com
Comparative Economic Sufficiency (CES) is used as a proxy for SES, given challenges in measuring socioeconomic status in Malaysian adolescents. This 3-item scale included respondent’s perception and awareness of their own and their family’s ability to afford basic daily needs, condition of the neighborhood they live in, and how they compare their economic status to other students in their school.
PWB Scale Development using Exploratory and Confirmatory Factor Analysis
Results
Correlations of all variables studied are in the hypothesized direction.
How did we determine the relationship between school support variables and wellbeing variables?
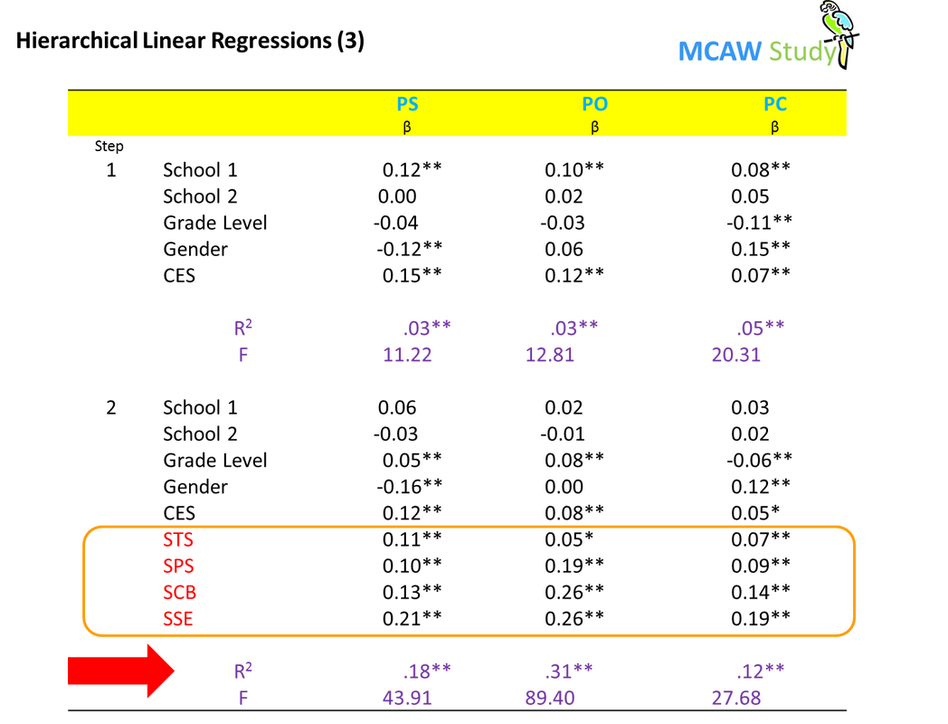
We used hierarchical linear regressions where in…..
•In Step 1, we control for the effects of school (school 3 acts as the reference), grade level, gender (boys = 0, girls = 1), and CES; and
•In Step 2, we add our School support variables.
There are 3 separate regression results shown in the table below:
We used hierarchical linear regressions where in…..
•In Step 1, we control for the effects of school (school 3 acts as the reference), grade level, gender (boys = 0, girls = 1), and CES; and
•In Step 2, we add our School support variables.
There are 3 separate regression results shown in the table below:
|
The above looks too complicated? Below is an easier way to see the results:
|
In all three regressions, the assumption for independent errors is tenable as Durbin-Watson values are close to 2. Multicollinearity is not detected as VIF values are all well below 10 and tolerance statistics all well above 0.2. Average VIF for each regression is not greater than 1. All regressions have 96% (or more) cases with standardized residuals within ±2. No outliers were detected with large enough leverage to influence the regressions.
|
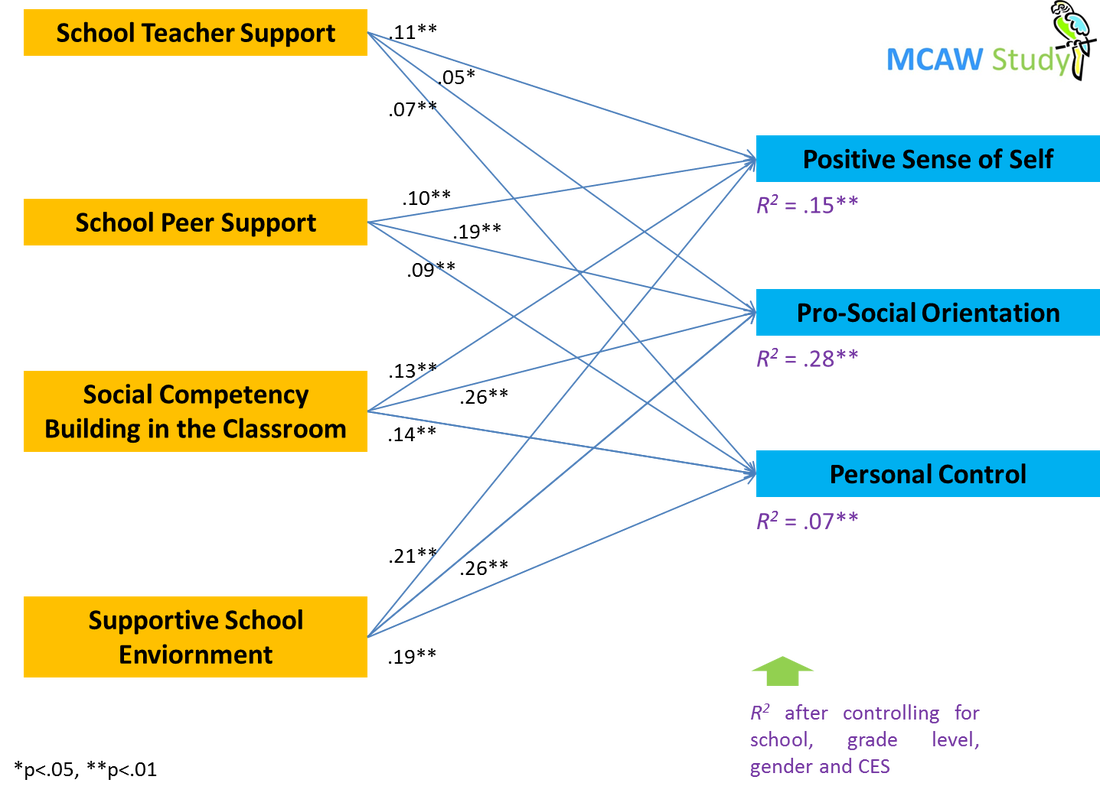
School supports account for
STS, SPS, SCB, and SSE are significantly associated with all three markers of adolescent wellbeing, with β-weights of .11, .10, .13, .21 for PS; .05, .19, .26, .26 for PO; and .07, .09, .14, .19 for PC.
For all three indicators of psychosocial well-being, there is very little variance explained by interaction variables entered in Step 3 of the regressions (ΔR2 = .01, .00, and .01 for positive sense of self, pro-social orientation, and resistance skills respectively; not shown in the table above). Meaning, gender does not moderate much the relationship between school supportiveness and the above three well-being markers.
- 15% of the variance for PS,
- 28% for PO, and
- 7% for PC.
STS, SPS, SCB, and SSE are significantly associated with all three markers of adolescent wellbeing, with β-weights of .11, .10, .13, .21 for PS; .05, .19, .26, .26 for PO; and .07, .09, .14, .19 for PC.
For all three indicators of psychosocial well-being, there is very little variance explained by interaction variables entered in Step 3 of the regressions (ΔR2 = .01, .00, and .01 for positive sense of self, pro-social orientation, and resistance skills respectively; not shown in the table above). Meaning, gender does not moderate much the relationship between school supportiveness and the above three well-being markers.
Discussion
References
Aalto-Setälä, T., Marttunen, M., Tuulio-Henriksson, A., Poikolainen, K., & Lönnqvist, J. (2002). Depressive symptoms in adolescence as predictors of early adulthood depressive disorders and maladjustment. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159, 1235 - 1237.
Ahmad, R. (1998). Educational development and reformation in Malaysia: past, present and future. Journal of Educational Administration, 36(5), 462 - 475.
Albee, G.W. & Gullotta, T.P. (Eds.)(1997). Primary Prevention Works. Issues in Children's and Families' Lives (Vol 6). Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Arbuckle, J.L. (2003). Amos 5.0 Update to the Amos User's Guide. Chicago: Smallwaters Corporation.
Arthur, M. W., Hawkins, J. D., Pollard, J. A., Catalano, R. F., & Baglioni, A. J. (2002). Measuring risk and protective factors for substance use, delinquency, and other adolescent problem behaviors: The Communities That Care Youth Survey. Evaluation Review, 26, 575 - 601.
Baker, J.A., Dilly, L.J., Aupperlee, J.L., and Patil, S.A. (2003). The developmental context of school satisfaction: Schools as psychologically healthy environments. School Psychology Quarterly, 18(2), 206 - 221.
Barone, T.N. (2004). Moral dimensions of teacher-student interactions in Malaysian secondary schools. Journal of Moral Education, 33(2), 179 - 196.
Barrera, M. (1986). Distinctions between social support concepts, measures, and models. American Journal of Community Psychology, 14, 413 - 445.
Battistich, V., Schapps, E., Watson, M., Solomon, D., & Lewis, C. (2000). Effects of the Child Development Project on students' drug use and other problem behaviors. Journal of Primary Prevention, 21, 75-99.
Battistich, V. (2000). The use of implementation data in assessing the effectiveness of the Child Development Project. Presented at the Society for Prevention Research Conference. June 2000. Montreal.
Battistich, V., Solomon, D., Watson, M., & Schapps, E. (1997). Caring school communities. Educational Psychologist, 32, 137-151.
Benson, P.L. (2002). Developmental assets and asset-building community: Conceptual and empirical foundations. In R.M. Lerner & P.L. Benson (eds.). Developmental assets and asset-building communities: Implications for research policy and practice. Norwell, MA: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Bentler, P.M. & Bonnett, D.G. (1980). Significance tests and goodness-of-fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychological Bulletin, 88, 588 - 600.
Bentler, P.M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 238 - 246.
Blechman, E.A., McEnroe, M.J., Carella, E.T., and Audette, D.P. (1986). Childhood competence and depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 95(3), 223 - 227.
Blum, R.W. & Libbey, H.P. (2004). Executive summary. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 231 - 232.
Blum, R. W. (2002). Positive youth development: A strategy for improving adolescent health. In R. M. Lerner, F. Jacobs & D. Wertlieb (Eds.), Handbook of Applied Developmental Science (Vol. 2, pp. 237-252). Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Bollen, K., and Lennox, R. (1991). Conventional wisdom on measurement: A structural equation perspective. Psychological Bulletin, 110(2), 305 – 314.
Botvin, G.L. (2000). Preventing drug abuse in schools: social and competence enhancement approaches targeting individual-level etiological factors. Addictive Behaviors, 25(6), 887 - 897.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Cambridge, MA: Havard University Press.
Brooks, T.L., Harris, S.K., Thrall, J.S., & Woods, E.R. (2002). Association of adolescent risk behaviors with mental health symptoms in high school students. Journal of Adolescent Health, 31, 240 - 246.
Brown, B.B., Dolcini, M.M., & Leventhal, A. (1997). Transformations in peer relationships at adolescence: Implications for health-related behavior. In J.Schulenberg, J.L. Maggs, & K. Hurrelmann (Eds.).Health risks and developmental transitions during adolescence (pp. 161 - 189). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In Bollen, K. A., & Long, J. S. (Eds.), Testing structural equation models (pp. 136-162). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Bryk, A.S. & Schnieder, B. (2002). Trust in schools: A core resource for improvement. New York: Sage.
Bukowski, W. (2003). Peer relationships. In M.H. Bornstein, L. Davidson, C.L.M. Keyes, & K.A. Moore (Eds.), Well-being: Positive development across the life course. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey.
Burns, J. and Hickie, I (2002). Depression in young people: A national school-based initiative for prevention, early intervention and pathways for care. Adolescent Psychiatry, 10(2), 134 – 138.
Call, K. T., Riedal, A. A., Hein, K., McLoyd, V., Petersen, A., & Kipke, M. (2002). Adolescent health and well-being in the twenty-first century: A global perspective. In R. W. Larson, B. B. Brown & J. T. Mortimer (Eds.), Adolescents' preparation for the future: Perils and promise (pp. 69-98): The Society for Research on Adolescence.
Caplan, M., Weissberg, R. P., Grober, J. S., Sivo, P. J., Grady, K., & Jacoby, C. (1992). Social competence promotion with inner-city and suburban young adolescents: Effects on social adjustment and alcohol use. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60(1), 56-63.
Carnegie Council on Adolescent Development. (1995). Great transitions: Preparing adolescents for a new century. Washington, DC: Carnegie Council on Adolescent Development.
Carnegie Council on Adolescent Development. (1989). Turning Points: Preparing American Youth for the 21st Century (Report of the Task Force on Education of Young Adolescents). New York: Carnegie Corporation.
Caspi, A., Lynam, D., Moffitt, T.E., & Silva, P.A. (1993). Unraveling girls' delinquency: biological, dispositional, and contextual contributions to adolescent misbehavior. Developmental Psychology, 29(1), 19 - 30.
Catalano, R.F., Haggerty, K.P., Oesterle, S., Fleming, C.B., & Hawkins, J.D. (2004). The importance of bonding to school for healthy development: findings from the social development research group. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 252 - 261.
Catalano, Berglund, Ryan, Lonczak, & Hawkins. (2002). Positive youth development in the United States: Research findings on evaluations of positive youth development programs. Prevention & Treatment, 5, Article 15.
Channing Bete (2001). Pennsylvania Youth Survey.
Chen, X., He, Y., and Li, D. (2004). Self-perceptions of social competence and self-worth in Chinese children: relations with social and school performance. Social Development, 13(4), 570 - 589.
Chok, S.L. (2005). More children seeking counseling. News Trait Times, May 29, 2005.
Clark, M.L. (1991). Social identity, peer relations, and academic competence of African-American adolescents. Education and Urban Society, 24, 41 – 52.
Coie, J.D. & Jacobs, M.R. (1993). The role of social context in the prevention of conduct disorder. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 263 - 275.
Community Health Bulletin: Special Issue, 2000. Retrieved on January 15, 2003, from http://www.commhlth.medic.ukm.my/penerbitan/buletin/khas00/
Compas, B., Ey, S., & Grant, K. (1993). Taxonomy, assessment, and diagnosis of depression during adolescence. Psychological Bulletin, 114, 323-344.
Conger, R.D., Conger, K.J., and Matthew, L.S. (1999). Pathways of economic influence on adolescent adjustment. American Journal of Community Psychology, 27(4), 519 - 541.
Costello, E. J., Pine, D. S., Hammen, C., March, J. S., Plotsky, P. M., Weissman, M. M., et al. (2002). Development and natural history of mood disorders,. Biological Psychiatry, 52(6), 529-542.
Cowen, E. L. (2000). Psychological wellness: Some hopes for the future. In D. Cicchetti, J. Rappaport, I. Sandler & R. P. WEissberg (Eds.), The promotion of wellness in children and adolescents. Washington, DC: CWLA Press.
Crosnoe, R, Johnson, M.K., Elder, G.H. (2004). Intergenerational bonding in school: The behavioral and contextual correlates of student-teacher relationships. Sociology of Education, 77(1), 60 – 81.
Crosnoe, R. & Elder, G.H. (2004). Family dynamics, supportive relationships, and educational resilience during adolescence. Journal of Family Issues, 25(5), 571 - 602.
Crosnoe, R. Cavanagh, S., and Elder, G.H. (2003). Adolescent friendships as academic resources: The intersection of friendship, race, and school disadvantage. Sociological Perspectives, 46(3), 331 – 352.
Dryfoos, J. (1998). Thirty years in pursuit of the magic bullet. Journal of Adolescent Health, 23, 338 - 343.
Dubow, E.F., Roeker, C., and D'Imperio (1997). Mental health. In R.T. Ammerman & M. Hersen (Eds.). Handbook of prevention and treatment with children and adolescents. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Dubow, E.F. and Ullman, D.G. (1989). Assessing social support in elementary school children: The survey of children's social support. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 18(1), 52 - 64.
Eccles, J. S., Midgley, C., Wigfield, A., Buchanan, C. M., Reuman, D., Flanagan, C. &
Mac Iver, D. (1993). Development during adolescence: The impact of stage
-environment fit on young adolescents' experiences in schools and in families.
Journal of the American Psychologist Association, 48, 90-101.
Erikson, E. (1968). Identity, Youth and Crisis. New York: W.W. Norton.
Furman, W. and Buhrmester, D. (1985). Children's perceptions of their personal relationships in their social networks. Developmental Psychology, 21(6), 1016 - 1024.
Gillham, J.E., Reivich, K.J., Jaycox, L.H., and Seligman, M.E. (1995). Prevention of depressive symptoms in schoolchildren: Two-year follow-up. Psychological Science, 6(6), 343 – 351.
Gomez, B.J. (2005a). Measuring psychosocial well-being in Malaysian adolescents. Manuscript in progress.
Gomez, B.J. (2005b). The two faces of psychosocial functioning in Malaysian school-going adolescents. Manuscript in progress.
Gomez, B.J. (2005c). Supportiveness and adolescent functioning in Malaysia: Psychosocial well-being. Manuscript in progress.
Gomez, B.J. (2005d). Supportiveness and adolescent functioning in Malaysia: Psychosocial maladjustment and educational outcomes. Manuscript in progress.
Gomez, B.J. & Ang, P.M.M. (2005). Promoting positive youth development in adolescents and creating system-wide change in schools. Manuscript in progress for publication in Theory & Practice.
Gottfredson, D.C. & Gottfredson, G.D. (2002). Quality of school-based prevention programs: results from a national survey. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 39(1), 3 - 35.
Greenberg, M. T., Weissberg, R. P., O' Brien, M. U., Zins, J. E., Fredericks, L., Resnik, H., et al. (2003). Enhancing school-based prevention and youth development through coordinated social, emotional, and academic learning. American Psychologist, 58(6/7), 466-474.
Haris, M.J. (1997). Values and citizenship education in Malaysia. In K.J.Kennedy (Ed.). Citizenship Education and the Modern State (pp. 96 - 106). London, Falmer Press. Cited in Liau, A.K., Liau, A.W., Teoh, G.B.S., Liau, M.T.L. (2003). The case for emotional literacy: the influence of emotional intelligence on problem behaviors in Malaysian secondary school students. Journal of Moral Education, 32(1), 51 - 66.
Harter, S. (1990). Identity and self development. In S. Feldman and G. Elliott (Eds.), At the threshold: The developing adolescent (pp. 352-387). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Harter, S (1985). Manual for the self-perception profile for children (revision of the perceived competence scale for children). Denver, CO: University of Denver.
Hartup, W. (1996). The company they keep. friendships and their developmental significance. Child Development, 67, 1 - 13.
Hawkins, J.D. (1999). Preventing crime and violence through Communities That Care. European Journal on Criminal Policy & Research, 7, 443 - 458
Hawkins, J.D., Catalano, R.F., and Miller, J.Y. (1992). Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: Implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 64 - 105.
Haynes, N.M., Emmons, C.L., Gebreyesus, S., and Ben-Avie, M. (1996). The School Development Program Evaluation Process. In J.P. Comer, N.M. Haynes, E.T. Joyner, and M. Ben-Avie (Eds.), Rallying the Whole Village: The Comer Process for Reforming Education (pp.123 – 146). New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Heaven, P.C., Newbury, K., and Mak, A. (2004). The impact of adolescent and parental characteristics on adolescent levels of delinquency and depression. Personality and Individual Differences, 36, 173 – 185.
Hoffman, M. A. , Levy-Shiff, R. & Ushpiz, V. (1993), Moderating effects of adolescent social orientation on the relation between social support and self-esteem. Journal of Youth & Adolescence, 22(1), 23 - 31.
Hughes, J.N., Cavell, T.A., and Grossman, P.B. (1997). A positive view of self: Risk and protection for aggressive children? Development and Psychopathology, 9(1), 75 -94.
Hunter, J. P., & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2003). The Positive Psychology of Interested Adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 32(1), 27-35.
Jabnoon, N & Chan, Y.F. (2001). Job satisfaction of secondary school teachers in Selangor, Malaysia. International Journal of Commerce and Management, 11(3/4), p72-90
Jessor, R., Turbin, M.S., and Costa, F.M. (1998). Protective factors in adolescent health behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75(3), 788 - 800
Kaur, P. (2000). People & Development Challenges, 6(12). Retrieved May 27, 2003, from http://www.ippf.org/regions/eseaor/pdc/vol6no12/ffpam.htm
Kazdin, A. (1989). Identifying depression in children: A comparison of alternative selection criteria. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 17, 436-454.
Kazdin, A.E. (1993). Adolescent mental health: Prevention and treatment programs. American Psychology, 48, 127 - 141.
Keyes, C. L., & Haidt, J. (2003). Flourishing: Positive psychology and the life well-lived. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Keyes, C. L., Ryff, C. D., & Shmotkin, D. (2002). Optimizing well-being: The empirical encounter of two traditions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 82(6), 1007-1022.
Khoo, K.C. (2002). Promoting the development of the ASEAN Child. In R.M. Lerner, F. Jacobs, & D. Wertlieb (Eds.). Handbook of Applied Developmental Science, 3(1), 287 - 308.
Klem, A.M. and Connell, J.P. (2004). Relationships matter: Linking teacher support to student engagement and achievement. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 262 - 273.
Krishnamoorthy, M. (2005). UiTM to conduct study on depression among students. STAR, May 18, 2005.
Kubic, M.Y., Lytle, L.A., Birnbaum, A.S., Murray, D.M., & Perr, C.L. (2003). Prevalence and correlates of depressive symptoms in young adolescents. American Journal of Health Behavior, 27(5), 546 - 553.
Kupermine, G.P., Leadbeater, B.J., and Blatt, S.J. (2001). School social climate and individual differences in vulnerability to psychopathology among middle school students. Journal of School Psychology, 39(2), 141 - 159.
Larson, R. W. (2000). Towards a psychology of positive youth development. American Psychologist, 55(1), 170-183.
Leffert, N., Benson, P. L., Scales, P. C., Sharma, A. R., Drake, D. R., & Blyth, D. A. (1998). Developmental assets: Measurement and prediction of risk behaviors among adolescents. Applied Developmental Science, 2(4), 209 - 230.
Lerner, R. M., & Castellino, D. R. (2002). Contemporary developmental theory and adolescence: Developmental systems and applied developmental science. Journal of Adolescent Health, 31(6), 122-135.
Lerner, R.M. & Galambos, N.L. (1998). Adolescent development: Challenges and opportunities for research, programs, and policies. Annual Review of Psychology, 49, 413 - 446.
Liau, A.K., Liau, A.W., Teoh, G.B.S., Liau, M.T.L. (2003). The case for emotional literacy: the influence of emotional intelligence on problem behaviors in Malaysian secondary school students. Journal of Moral Education, 32(1), 51 - 66.
Libbey, H.P. (2004). Measuring student relationships to school: Attachment, bonding, connectedness, and engagement. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 274 - 283.
Malaysia (1997). Executive summary report on current social issues. Paper presented by The Chief Secretary, Ministry of National Unity and Community Development, Malaysia, Brainstorming Session on Social Issues and Problems in the State of Johor), Kota Tinggi, Johor, Malaysia (6-8 March). Cited in Yusof, S.A. & Amin, R.M. (1999). Admired values: The case of teenagers in Malaysia. The International Journal of Social Economics, 26(6), 802 -
Malaysian Department of Statistics (2004). Population by sex, ethnic group and age, W.P. Kuala Lumpur. Personal Communication.
Maria, M.S. (2002). Youth in Southeast Asia: Living within the continuity of tradition and the turbulence of change. In B. Bradford, R.W. Larson, T.S. Saraswathi (Eds.), The World's Youth: Adolescence in Eight regions of the Globe. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Marsh, H.W. & Shavelson, R. (1985). Self-concept: its multifaceted, hierarchical structure. Educational Psychologist, 20(3), 107 - 123.
Masten, A., S., & Coatsworth, J. D. (1998). The development of competence in favorable and unfavorable environments: Lessons from research on successful children. American Psychologist, 53, 205-220.
McLeod, J. D. & Owens, T. J. (2004). Psychological well-being in the early life course: Variations by socioeconomic status, gender, and race/ethnicity. Social Psychology Quarterly, 67(3), 257 - 278.
McLoyd, V.C. (1998). Socioeconomic disadvantage and child development. American Psychologist, 53(2), 185 - 204.
McNeely, C. & Falci, C. (2004). School connectedness and the transition into and out of health-risk behavior among adolescents: A comparison of social belonging and teacher support. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 284 - 292.
Meredith, W. (1993). Measurement invariance, factor analysis and factorial invariance, Psychometrika, 58, 525 - 543.
Ministry of Education (2004). The development of education: National report of Malaysia. Report submitted to The International Bureau of Education, UNESCO on 31st July 2004.
Moffit, T.E. (1993). Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: A developmental taxonomy. Psychological Review, 100(4), 674 - 710.
Moore, K. A., Evans, V.J., Brooks-Gunn, J. & Roth J. (2001). What are good child outcomes? In A.T. Thornton (Ed), The Well-being of Children and Families: Research and Data Needs. Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press.
Muthen, B.O. (1994). Multilevel covariance structure analysis. Sociological Methods and Research, 22, 376 – 398.
National Advisory Mental Health Council (1990). National plan for research on child and adolescent mental disorders. DHHS Publication No. 90-1683. Cited in Greenberg, M.T., Domitrovich, C., and Bumbarger, B. (1999). Preventing mental disorders in school-age children: A review of the effectiveness of prevention programs. Report to Center for Mental Health Services (CMHS), Substance Abuse Mental Health Services Administration. Obtainable online from the Prevention Research Center (Pennsylvania State University) at www.psu.edu/dept/prevention.
National Research Council, & Institute of Medicine. (2002). Community Programs to Promote Youth Development. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
National Office for Human Development (2000). Programme Approach in the Context of Malaysia. Catholic Welfare Services. National Office for Human Development, Malaysia.
Neter, J., Kutner, M.H., Nachtsheim, C.J., & Wasserman, W. (1996). Applied Linear Statistical Models: 4th Edition. McGraw-Hill.
Newman, B.M. & Newman, P.R. (1987). The impact of high school on social development. Adolescence, 22, 526 - 534
New Straits Times (2004). Mental illness among teenagers on the rise. September 18, 2004.
New Strait Times (2000). Mental health plans for youths neglected. June 7, 2000.
Olsson, C.A., Bond, L., Burns, J.M., Vella-Brodrick, D.A., & Sawyer, S.M. (2002). Adolescent resilience: a concept analysis. Journal of Adolescence, 26, 1 - 11.
Overbeek, G., Vollebergh, W., Meeus, W, Engels, R, & Luijpers, E. (2001). Course, co-occurrence, and longitudinal associations of emotional disturbance and delinquency from adolescence to young adulthood: A six-year three-wave study. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 30(4), 401 – 426.
Park, N. (2004). Character strengths and positive youth development. The Annals of The Americal Academy of Political and Social Science, 591, 25 -39.
Pawelko, K. A., and Magafas, A.H. (1997). Leisure well-being among adolescent groups: time, choices and self-determination. Research Update, July, 26 – 34.
Payne, A. A., Gottfredson, D.C., and Gottfredson, G.D. (2003). Schools as communities: The relationships among communal school organization, student bonding, and school disorder. Criminology, 41(3), 749 – 777.
Pitman, K., Irby, M., & Ferber, T. (2000). Unfinished business: Further reflections on a decade of promoting youth development. In Youth Development: Issues, Challenges and Directions. Philadelphia: Public/Private Ventures.
Pollard, J. A., Hawkins, J. D., & Arthur, M. W. (1999). Risk and protection: Are both necessary to understand diverse behavioral outcomes in adolescence? Social Work Research, 23, 145-157.
Pong, S.L. (1995). Access to education in Peninsular Malaysia: ethnicity, social class and gender. Compare, 25(3), 239 - 252.
Procidano, M.E. and Heller, K. (1983). Measures of perceived social support from friends and from family: Three validation studies. American Journal of Community Psychology, 11(1), 1 – 24.
Resnick, M.D., Bearman, P.S., Blum, R.W., Bauman, K.E. et al. (1997). Protecting adolescents from harm: findings from the National Lonitudinal Study on Adolescent Health. JAMA, 278(10), 823 -832.
Richman, J.M., and Bowen, G.L. (1997). School failure: An ecological-interactional-developmental perspective. In M.W. Fraser (Ed.), Risk and resilience in childhood: An ecological perspective (pp. 95 – 116). Washington, DC: NASW Press. Cited in Rosenfeld, L.B., Richman, J.M., Bowen, G.L. (1998). Low Social Support among at-risk adolescents. Social Work in Education, 20(4), 245 – 260.
Roberts, M.C., Brown, K.J., Johnson, R.J., & Reinke, J. (2002). Positive psychology for children: development, prevention, and promotion. In C. R. Snyder & S. Lopez (Eds.), Handbook of positive psychology (pp. 663-675). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Roeser, R. W., Eccles, J. S., & Sameroff, A. J. (2000). School as a context of early adolescents' academic and social-emotional development: A summary of research findings. Elementary School Journal, 100(5), 443-471.
Rolf, J. E., & Johnson, J. L. (1999). Opening doors to resilience intervention for
prevention research. In M. D. Glantz and J. L. Johnson (Eds.), Resiliency and development: Positive life adaptations (pp. 229-249). New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers.
Rosenfeld, L.B., Richman, J.M., Bowen, G.L. (2000). Social support networks and school outcomes: The centrality of the teacher. Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal, 17(3), 205 -226.
Rosenfeld, L.B., Richman, J.M., Bowen, G.L. (1998). Low Social Support among at-risk adolescents. Social Work in Education, 20(4), 245 – 260.
Roth, J., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2002). What is a youth development program? Identification of defining principles. In R. M. Lerner, F. Jacobs & D. Wertlieb (Eds.), Handbook of Applied Developmental Science (Vol. 2, pp. 197-223). Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Roth, J., Brooks-Gunn, J., Murray, L., & Foster, W. (1998). Promoting health adolescents: Synthesis of youth development program evaluations. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 8(4), 423-459.
Rutter, M. (1997). Comorbidity: concepts, claims and choices. Criminal Behavior and Mental Health, 7, 279 - 285.
Rutter, M. (1979). Protective factors in children’s responses to stress and disadvantage. In M.W. Kent and J.E. Rolf (Eds.), Primary prevention of psychopathology: Social competence in children (pp. 49 – 74). Hanover, NH: University Press of New England. Cited in Rosenfeld, L.B., Richman, J.M., Bowen, G.L. (1998). Low Social Support among at-risk adolescents. Social Work in Education, 20(4), 245 – 260.
Ryff, C. D. (1995). Psychological well-being in adult life. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 4, 99-104.
Ryff, C. D. (1989). Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological wellbeing. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 57, 1069 -1081.
Samdal, O., Nutbeam, D., Wold, B., and Kannas, L. (1998). Achieving health and educational goals through schools - a study of the importance of the school climate and the students' satisfaction with school. Health Education Research, 13(3), 383 - 397.
Sameroff, A. J. (2000). Developmental systems and psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 297-312. Scales, P.C., and Leffert, N. (Eds.), (1999). Developmental Assets: A Synthesis of the Scientific Research on Adolescent Development. Search Institute.
Sawyer, M. G., Arney, F., Baghurst, P., Clark, J.J., Graetz, B. W., Kosky, R. J., Nurcombe, B., Patton, G.C., Prior M.R., Raphael, B. Rey, J., Whaites, L.C., and Zubrick, S. R. (2000). The Mental Health of Young People in Australia. Mental Health and Special Programs Branch, Commonwealth Department of Health and Aged Care, Canberra.
Scales, P.C., and Leffert, N. (Eds.), (1999). Developmental Assets: A Synthesis of the Scientific Research on Adolescent Development. Search Institute.
Seals, D. and Young. J. (2003). Bullying and victimization: prevalence and relationship to gender, grade level, ethnicity, self-esteem, and depression. Adolescence, 38(152), 735 - 747.
Search Institute (2003). Developmental Assets Checklist. Personal Communication.
Seligman, M. P. (2002). Positive psychology, positive prevention, and positive therapy. In C. R. Snyder & S. J. Lopez (Eds.), Handbook of positive psychology (pp. 3-9). London: Oxford University Press.
Sennyah, P., Chow, K.H., & Mohamad, S.G. (2000). Mental Act to be amended. In New Strait Times, October 23, 2000.
Schneider, B.H. (1998). Cross-cultural comparison as doorkeeper in research on the social and emotional adjustment of children and adolescents. Developmental Psychology, 34(4), 793 - 797.
Solomon, D., Battistich, V., Watson, M., Schaps, E., and Lewis, C. (2000). A six-district study of educational change: direct and mediated effects of the child development project. School Psychology of Education, 4, 3 - 51.
Steiger, J.H. (1990). Structural model evaluation and modification: an internal estimation approach. Multivariate Behavioural Research, 25, 173 - 180.
Steinberg, L. & Morris, A.S. (2001). Adolescent development. Annual Review of Psychology, 52, 83 - 110.
Stewart, E. A. (2003). School social bonds, school climate, and school misbehavior: A multilevel analysis. Justice Quarterly, 20(3), 575 – 604.
Takakura, M. & Sakihara, S. (2001). Psychological correlates of depressive symptoms among Japanese high school students. Journal of Adolescent Health, 28, 82 – 89.
Tobler, N. S., Roona, M. R., Ochshorn, P., Marshall, D. G., Streke, A. V., & Stackpole, K. M. (2000). School based adolescent drug prevention programs: 1998 meta-analysis. Journal of Primary Prevention, 20, 275-336.
Tucker, L.R. & Lewis, C. (1973). A reliability coefficient for maximum likelihood factor analysis. Psychometrika, 38, 1 - 10.
Tygart, C. (1998). Public school vandalism: Towards a synthesis of theories and transition to paradigm analysis. Adolescence, 23(89), 187 – 200.
Wang M. C., Haertel, G. D., & Walberg,, H. J. (1999). Psychological and Educational Resilience. In A. J. Reynolds, H. J. Walberg, and R. P. Weissberg (Eds.), Promoting positive outcomes: Issues in children’s and families’ lives. Washington, DC: Child Welfare League of America.
Weissberg, R. P., & Greenberg, M. T. (1998). School and community competence-enhancement and prevention programs. In I. E. Sigel & K. A. Renninger (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology (5th ed., Vol. 4: Child psychology in practice, pp. 877-954). New York: Wiley.Welsh, J.A. & Bierman, K.L. (2001). Mastering the social, emotional, and cognitive skills and behaviors needed to succeed as a member of society. Gale Encyclopedia of Childhood and Adolescence. Retrieved on May 27, 2003, from http://www.findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_g2602/is_0004/ai_2602000487
Werner, E.E. (1995). Resilience in Development. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 4(3), 81 – 85.
Werner, E. E. (1993). Risk, resilience, and recovery: Perspectives from the Kauai Longitudinal Study. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 503-515.
Wilkinson, R. B., & Walford, W. A. (1998). The measurement of adolescent psychological health: One or two dimensions? Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 27(4), 443 - 455.
Wilson, D. (2004). The interface of school climate and school connectedness and relationships with aggression and victimization. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 293 – 299.
World Data on Education (2004). National report on the development of education: Malaysia. Prepared for the International Bureau of Education. Retrieved on May 27, 2004, from http://www.ibe.unesco.org/International/Databanks/Wde/profilee.htm
Yusof, S.A. & Amin, R.M. (1999). Admired values: The case of teenagers in Malaysia. The International Journal of Social Economics, 26(6), 802 -
Zaff, J.F., Smith, D.C., Rogers, M.F., Halle, T.G., & Bornstein, M.H. (2003). Holistic well-being and the developing child. In M.H. Bornstein, L. Davidson, C.L.M. Keyes, & K.A. Moore (Eds.), Well-being: Positive development across the life course. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey.
Zaff, J.F. and Hair, E.C. (2003). Positive development of the self: Self-concept, self-esteem, and identity. In M.H. Bornstein, L. Davidson, C.L.M. Keyes, & K.A. Moore (Eds.), Well-being: Positive development across the life course. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey.
Ahmad, R. (1998). Educational development and reformation in Malaysia: past, present and future. Journal of Educational Administration, 36(5), 462 - 475.
Albee, G.W. & Gullotta, T.P. (Eds.)(1997). Primary Prevention Works. Issues in Children's and Families' Lives (Vol 6). Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Arbuckle, J.L. (2003). Amos 5.0 Update to the Amos User's Guide. Chicago: Smallwaters Corporation.
Arthur, M. W., Hawkins, J. D., Pollard, J. A., Catalano, R. F., & Baglioni, A. J. (2002). Measuring risk and protective factors for substance use, delinquency, and other adolescent problem behaviors: The Communities That Care Youth Survey. Evaluation Review, 26, 575 - 601.
Baker, J.A., Dilly, L.J., Aupperlee, J.L., and Patil, S.A. (2003). The developmental context of school satisfaction: Schools as psychologically healthy environments. School Psychology Quarterly, 18(2), 206 - 221.
Barone, T.N. (2004). Moral dimensions of teacher-student interactions in Malaysian secondary schools. Journal of Moral Education, 33(2), 179 - 196.
Barrera, M. (1986). Distinctions between social support concepts, measures, and models. American Journal of Community Psychology, 14, 413 - 445.
Battistich, V., Schapps, E., Watson, M., Solomon, D., & Lewis, C. (2000). Effects of the Child Development Project on students' drug use and other problem behaviors. Journal of Primary Prevention, 21, 75-99.
Battistich, V. (2000). The use of implementation data in assessing the effectiveness of the Child Development Project. Presented at the Society for Prevention Research Conference. June 2000. Montreal.
Battistich, V., Solomon, D., Watson, M., & Schapps, E. (1997). Caring school communities. Educational Psychologist, 32, 137-151.
Benson, P.L. (2002). Developmental assets and asset-building community: Conceptual and empirical foundations. In R.M. Lerner & P.L. Benson (eds.). Developmental assets and asset-building communities: Implications for research policy and practice. Norwell, MA: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Bentler, P.M. & Bonnett, D.G. (1980). Significance tests and goodness-of-fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychological Bulletin, 88, 588 - 600.
Bentler, P.M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 238 - 246.
Blechman, E.A., McEnroe, M.J., Carella, E.T., and Audette, D.P. (1986). Childhood competence and depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 95(3), 223 - 227.
Blum, R.W. & Libbey, H.P. (2004). Executive summary. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 231 - 232.
Blum, R. W. (2002). Positive youth development: A strategy for improving adolescent health. In R. M. Lerner, F. Jacobs & D. Wertlieb (Eds.), Handbook of Applied Developmental Science (Vol. 2, pp. 237-252). Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Bollen, K., and Lennox, R. (1991). Conventional wisdom on measurement: A structural equation perspective. Psychological Bulletin, 110(2), 305 – 314.
Botvin, G.L. (2000). Preventing drug abuse in schools: social and competence enhancement approaches targeting individual-level etiological factors. Addictive Behaviors, 25(6), 887 - 897.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Cambridge, MA: Havard University Press.
Brooks, T.L., Harris, S.K., Thrall, J.S., & Woods, E.R. (2002). Association of adolescent risk behaviors with mental health symptoms in high school students. Journal of Adolescent Health, 31, 240 - 246.
Brown, B.B., Dolcini, M.M., & Leventhal, A. (1997). Transformations in peer relationships at adolescence: Implications for health-related behavior. In J.Schulenberg, J.L. Maggs, & K. Hurrelmann (Eds.).Health risks and developmental transitions during adolescence (pp. 161 - 189). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In Bollen, K. A., & Long, J. S. (Eds.), Testing structural equation models (pp. 136-162). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Bryk, A.S. & Schnieder, B. (2002). Trust in schools: A core resource for improvement. New York: Sage.
Bukowski, W. (2003). Peer relationships. In M.H. Bornstein, L. Davidson, C.L.M. Keyes, & K.A. Moore (Eds.), Well-being: Positive development across the life course. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey.
Burns, J. and Hickie, I (2002). Depression in young people: A national school-based initiative for prevention, early intervention and pathways for care. Adolescent Psychiatry, 10(2), 134 – 138.
Call, K. T., Riedal, A. A., Hein, K., McLoyd, V., Petersen, A., & Kipke, M. (2002). Adolescent health and well-being in the twenty-first century: A global perspective. In R. W. Larson, B. B. Brown & J. T. Mortimer (Eds.), Adolescents' preparation for the future: Perils and promise (pp. 69-98): The Society for Research on Adolescence.
Caplan, M., Weissberg, R. P., Grober, J. S., Sivo, P. J., Grady, K., & Jacoby, C. (1992). Social competence promotion with inner-city and suburban young adolescents: Effects on social adjustment and alcohol use. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60(1), 56-63.
Carnegie Council on Adolescent Development. (1995). Great transitions: Preparing adolescents for a new century. Washington, DC: Carnegie Council on Adolescent Development.
Carnegie Council on Adolescent Development. (1989). Turning Points: Preparing American Youth for the 21st Century (Report of the Task Force on Education of Young Adolescents). New York: Carnegie Corporation.
Caspi, A., Lynam, D., Moffitt, T.E., & Silva, P.A. (1993). Unraveling girls' delinquency: biological, dispositional, and contextual contributions to adolescent misbehavior. Developmental Psychology, 29(1), 19 - 30.
Catalano, R.F., Haggerty, K.P., Oesterle, S., Fleming, C.B., & Hawkins, J.D. (2004). The importance of bonding to school for healthy development: findings from the social development research group. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 252 - 261.
Catalano, Berglund, Ryan, Lonczak, & Hawkins. (2002). Positive youth development in the United States: Research findings on evaluations of positive youth development programs. Prevention & Treatment, 5, Article 15.
Channing Bete (2001). Pennsylvania Youth Survey.
Chen, X., He, Y., and Li, D. (2004). Self-perceptions of social competence and self-worth in Chinese children: relations with social and school performance. Social Development, 13(4), 570 - 589.
Chok, S.L. (2005). More children seeking counseling. News Trait Times, May 29, 2005.
Clark, M.L. (1991). Social identity, peer relations, and academic competence of African-American adolescents. Education and Urban Society, 24, 41 – 52.
Coie, J.D. & Jacobs, M.R. (1993). The role of social context in the prevention of conduct disorder. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 263 - 275.
Community Health Bulletin: Special Issue, 2000. Retrieved on January 15, 2003, from http://www.commhlth.medic.ukm.my/penerbitan/buletin/khas00/
Compas, B., Ey, S., & Grant, K. (1993). Taxonomy, assessment, and diagnosis of depression during adolescence. Psychological Bulletin, 114, 323-344.
Conger, R.D., Conger, K.J., and Matthew, L.S. (1999). Pathways of economic influence on adolescent adjustment. American Journal of Community Psychology, 27(4), 519 - 541.
Costello, E. J., Pine, D. S., Hammen, C., March, J. S., Plotsky, P. M., Weissman, M. M., et al. (2002). Development and natural history of mood disorders,. Biological Psychiatry, 52(6), 529-542.
Cowen, E. L. (2000). Psychological wellness: Some hopes for the future. In D. Cicchetti, J. Rappaport, I. Sandler & R. P. WEissberg (Eds.), The promotion of wellness in children and adolescents. Washington, DC: CWLA Press.
Crosnoe, R, Johnson, M.K., Elder, G.H. (2004). Intergenerational bonding in school: The behavioral and contextual correlates of student-teacher relationships. Sociology of Education, 77(1), 60 – 81.
Crosnoe, R. & Elder, G.H. (2004). Family dynamics, supportive relationships, and educational resilience during adolescence. Journal of Family Issues, 25(5), 571 - 602.
Crosnoe, R. Cavanagh, S., and Elder, G.H. (2003). Adolescent friendships as academic resources: The intersection of friendship, race, and school disadvantage. Sociological Perspectives, 46(3), 331 – 352.
Dryfoos, J. (1998). Thirty years in pursuit of the magic bullet. Journal of Adolescent Health, 23, 338 - 343.
Dubow, E.F., Roeker, C., and D'Imperio (1997). Mental health. In R.T. Ammerman & M. Hersen (Eds.). Handbook of prevention and treatment with children and adolescents. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Dubow, E.F. and Ullman, D.G. (1989). Assessing social support in elementary school children: The survey of children's social support. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 18(1), 52 - 64.
Eccles, J. S., Midgley, C., Wigfield, A., Buchanan, C. M., Reuman, D., Flanagan, C. &
Mac Iver, D. (1993). Development during adolescence: The impact of stage
-environment fit on young adolescents' experiences in schools and in families.
Journal of the American Psychologist Association, 48, 90-101.
Erikson, E. (1968). Identity, Youth and Crisis. New York: W.W. Norton.
Furman, W. and Buhrmester, D. (1985). Children's perceptions of their personal relationships in their social networks. Developmental Psychology, 21(6), 1016 - 1024.
Gillham, J.E., Reivich, K.J., Jaycox, L.H., and Seligman, M.E. (1995). Prevention of depressive symptoms in schoolchildren: Two-year follow-up. Psychological Science, 6(6), 343 – 351.
Gomez, B.J. (2005a). Measuring psychosocial well-being in Malaysian adolescents. Manuscript in progress.
Gomez, B.J. (2005b). The two faces of psychosocial functioning in Malaysian school-going adolescents. Manuscript in progress.
Gomez, B.J. (2005c). Supportiveness and adolescent functioning in Malaysia: Psychosocial well-being. Manuscript in progress.
Gomez, B.J. (2005d). Supportiveness and adolescent functioning in Malaysia: Psychosocial maladjustment and educational outcomes. Manuscript in progress.
Gomez, B.J. & Ang, P.M.M. (2005). Promoting positive youth development in adolescents and creating system-wide change in schools. Manuscript in progress for publication in Theory & Practice.
Gottfredson, D.C. & Gottfredson, G.D. (2002). Quality of school-based prevention programs: results from a national survey. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 39(1), 3 - 35.
Greenberg, M. T., Weissberg, R. P., O' Brien, M. U., Zins, J. E., Fredericks, L., Resnik, H., et al. (2003). Enhancing school-based prevention and youth development through coordinated social, emotional, and academic learning. American Psychologist, 58(6/7), 466-474.
Haris, M.J. (1997). Values and citizenship education in Malaysia. In K.J.Kennedy (Ed.). Citizenship Education and the Modern State (pp. 96 - 106). London, Falmer Press. Cited in Liau, A.K., Liau, A.W., Teoh, G.B.S., Liau, M.T.L. (2003). The case for emotional literacy: the influence of emotional intelligence on problem behaviors in Malaysian secondary school students. Journal of Moral Education, 32(1), 51 - 66.
Harter, S. (1990). Identity and self development. In S. Feldman and G. Elliott (Eds.), At the threshold: The developing adolescent (pp. 352-387). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Harter, S (1985). Manual for the self-perception profile for children (revision of the perceived competence scale for children). Denver, CO: University of Denver.
Hartup, W. (1996). The company they keep. friendships and their developmental significance. Child Development, 67, 1 - 13.
Hawkins, J.D. (1999). Preventing crime and violence through Communities That Care. European Journal on Criminal Policy & Research, 7, 443 - 458
Hawkins, J.D., Catalano, R.F., and Miller, J.Y. (1992). Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: Implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 64 - 105.
Haynes, N.M., Emmons, C.L., Gebreyesus, S., and Ben-Avie, M. (1996). The School Development Program Evaluation Process. In J.P. Comer, N.M. Haynes, E.T. Joyner, and M. Ben-Avie (Eds.), Rallying the Whole Village: The Comer Process for Reforming Education (pp.123 – 146). New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
Heaven, P.C., Newbury, K., and Mak, A. (2004). The impact of adolescent and parental characteristics on adolescent levels of delinquency and depression. Personality and Individual Differences, 36, 173 – 185.
Hoffman, M. A. , Levy-Shiff, R. & Ushpiz, V. (1993), Moderating effects of adolescent social orientation on the relation between social support and self-esteem. Journal of Youth & Adolescence, 22(1), 23 - 31.
Hughes, J.N., Cavell, T.A., and Grossman, P.B. (1997). A positive view of self: Risk and protection for aggressive children? Development and Psychopathology, 9(1), 75 -94.
Hunter, J. P., & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2003). The Positive Psychology of Interested Adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 32(1), 27-35.
Jabnoon, N & Chan, Y.F. (2001). Job satisfaction of secondary school teachers in Selangor, Malaysia. International Journal of Commerce and Management, 11(3/4), p72-90
Jessor, R., Turbin, M.S., and Costa, F.M. (1998). Protective factors in adolescent health behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75(3), 788 - 800
Kaur, P. (2000). People & Development Challenges, 6(12). Retrieved May 27, 2003, from http://www.ippf.org/regions/eseaor/pdc/vol6no12/ffpam.htm
Kazdin, A. (1989). Identifying depression in children: A comparison of alternative selection criteria. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 17, 436-454.
Kazdin, A.E. (1993). Adolescent mental health: Prevention and treatment programs. American Psychology, 48, 127 - 141.
Keyes, C. L., & Haidt, J. (2003). Flourishing: Positive psychology and the life well-lived. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Keyes, C. L., Ryff, C. D., & Shmotkin, D. (2002). Optimizing well-being: The empirical encounter of two traditions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 82(6), 1007-1022.
Khoo, K.C. (2002). Promoting the development of the ASEAN Child. In R.M. Lerner, F. Jacobs, & D. Wertlieb (Eds.). Handbook of Applied Developmental Science, 3(1), 287 - 308.
Klem, A.M. and Connell, J.P. (2004). Relationships matter: Linking teacher support to student engagement and achievement. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 262 - 273.
Krishnamoorthy, M. (2005). UiTM to conduct study on depression among students. STAR, May 18, 2005.
Kubic, M.Y., Lytle, L.A., Birnbaum, A.S., Murray, D.M., & Perr, C.L. (2003). Prevalence and correlates of depressive symptoms in young adolescents. American Journal of Health Behavior, 27(5), 546 - 553.
Kupermine, G.P., Leadbeater, B.J., and Blatt, S.J. (2001). School social climate and individual differences in vulnerability to psychopathology among middle school students. Journal of School Psychology, 39(2), 141 - 159.
Larson, R. W. (2000). Towards a psychology of positive youth development. American Psychologist, 55(1), 170-183.
Leffert, N., Benson, P. L., Scales, P. C., Sharma, A. R., Drake, D. R., & Blyth, D. A. (1998). Developmental assets: Measurement and prediction of risk behaviors among adolescents. Applied Developmental Science, 2(4), 209 - 230.
Lerner, R. M., & Castellino, D. R. (2002). Contemporary developmental theory and adolescence: Developmental systems and applied developmental science. Journal of Adolescent Health, 31(6), 122-135.
Lerner, R.M. & Galambos, N.L. (1998). Adolescent development: Challenges and opportunities for research, programs, and policies. Annual Review of Psychology, 49, 413 - 446.
Liau, A.K., Liau, A.W., Teoh, G.B.S., Liau, M.T.L. (2003). The case for emotional literacy: the influence of emotional intelligence on problem behaviors in Malaysian secondary school students. Journal of Moral Education, 32(1), 51 - 66.
Libbey, H.P. (2004). Measuring student relationships to school: Attachment, bonding, connectedness, and engagement. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 274 - 283.
Malaysia (1997). Executive summary report on current social issues. Paper presented by The Chief Secretary, Ministry of National Unity and Community Development, Malaysia, Brainstorming Session on Social Issues and Problems in the State of Johor), Kota Tinggi, Johor, Malaysia (6-8 March). Cited in Yusof, S.A. & Amin, R.M. (1999). Admired values: The case of teenagers in Malaysia. The International Journal of Social Economics, 26(6), 802 -
Malaysian Department of Statistics (2004). Population by sex, ethnic group and age, W.P. Kuala Lumpur. Personal Communication.
Maria, M.S. (2002). Youth in Southeast Asia: Living within the continuity of tradition and the turbulence of change. In B. Bradford, R.W. Larson, T.S. Saraswathi (Eds.), The World's Youth: Adolescence in Eight regions of the Globe. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Marsh, H.W. & Shavelson, R. (1985). Self-concept: its multifaceted, hierarchical structure. Educational Psychologist, 20(3), 107 - 123.
Masten, A., S., & Coatsworth, J. D. (1998). The development of competence in favorable and unfavorable environments: Lessons from research on successful children. American Psychologist, 53, 205-220.
McLeod, J. D. & Owens, T. J. (2004). Psychological well-being in the early life course: Variations by socioeconomic status, gender, and race/ethnicity. Social Psychology Quarterly, 67(3), 257 - 278.
McLoyd, V.C. (1998). Socioeconomic disadvantage and child development. American Psychologist, 53(2), 185 - 204.
McNeely, C. & Falci, C. (2004). School connectedness and the transition into and out of health-risk behavior among adolescents: A comparison of social belonging and teacher support. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 284 - 292.
Meredith, W. (1993). Measurement invariance, factor analysis and factorial invariance, Psychometrika, 58, 525 - 543.
Ministry of Education (2004). The development of education: National report of Malaysia. Report submitted to The International Bureau of Education, UNESCO on 31st July 2004.
Moffit, T.E. (1993). Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: A developmental taxonomy. Psychological Review, 100(4), 674 - 710.
Moore, K. A., Evans, V.J., Brooks-Gunn, J. & Roth J. (2001). What are good child outcomes? In A.T. Thornton (Ed), The Well-being of Children and Families: Research and Data Needs. Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press.
Muthen, B.O. (1994). Multilevel covariance structure analysis. Sociological Methods and Research, 22, 376 – 398.
National Advisory Mental Health Council (1990). National plan for research on child and adolescent mental disorders. DHHS Publication No. 90-1683. Cited in Greenberg, M.T., Domitrovich, C., and Bumbarger, B. (1999). Preventing mental disorders in school-age children: A review of the effectiveness of prevention programs. Report to Center for Mental Health Services (CMHS), Substance Abuse Mental Health Services Administration. Obtainable online from the Prevention Research Center (Pennsylvania State University) at www.psu.edu/dept/prevention.
National Research Council, & Institute of Medicine. (2002). Community Programs to Promote Youth Development. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
National Office for Human Development (2000). Programme Approach in the Context of Malaysia. Catholic Welfare Services. National Office for Human Development, Malaysia.
Neter, J., Kutner, M.H., Nachtsheim, C.J., & Wasserman, W. (1996). Applied Linear Statistical Models: 4th Edition. McGraw-Hill.
Newman, B.M. & Newman, P.R. (1987). The impact of high school on social development. Adolescence, 22, 526 - 534
New Straits Times (2004). Mental illness among teenagers on the rise. September 18, 2004.
New Strait Times (2000). Mental health plans for youths neglected. June 7, 2000.
Olsson, C.A., Bond, L., Burns, J.M., Vella-Brodrick, D.A., & Sawyer, S.M. (2002). Adolescent resilience: a concept analysis. Journal of Adolescence, 26, 1 - 11.
Overbeek, G., Vollebergh, W., Meeus, W, Engels, R, & Luijpers, E. (2001). Course, co-occurrence, and longitudinal associations of emotional disturbance and delinquency from adolescence to young adulthood: A six-year three-wave study. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 30(4), 401 – 426.
Park, N. (2004). Character strengths and positive youth development. The Annals of The Americal Academy of Political and Social Science, 591, 25 -39.
Pawelko, K. A., and Magafas, A.H. (1997). Leisure well-being among adolescent groups: time, choices and self-determination. Research Update, July, 26 – 34.
Payne, A. A., Gottfredson, D.C., and Gottfredson, G.D. (2003). Schools as communities: The relationships among communal school organization, student bonding, and school disorder. Criminology, 41(3), 749 – 777.
Pitman, K., Irby, M., & Ferber, T. (2000). Unfinished business: Further reflections on a decade of promoting youth development. In Youth Development: Issues, Challenges and Directions. Philadelphia: Public/Private Ventures.
Pollard, J. A., Hawkins, J. D., & Arthur, M. W. (1999). Risk and protection: Are both necessary to understand diverse behavioral outcomes in adolescence? Social Work Research, 23, 145-157.
Pong, S.L. (1995). Access to education in Peninsular Malaysia: ethnicity, social class and gender. Compare, 25(3), 239 - 252.
Procidano, M.E. and Heller, K. (1983). Measures of perceived social support from friends and from family: Three validation studies. American Journal of Community Psychology, 11(1), 1 – 24.
Resnick, M.D., Bearman, P.S., Blum, R.W., Bauman, K.E. et al. (1997). Protecting adolescents from harm: findings from the National Lonitudinal Study on Adolescent Health. JAMA, 278(10), 823 -832.
Richman, J.M., and Bowen, G.L. (1997). School failure: An ecological-interactional-developmental perspective. In M.W. Fraser (Ed.), Risk and resilience in childhood: An ecological perspective (pp. 95 – 116). Washington, DC: NASW Press. Cited in Rosenfeld, L.B., Richman, J.M., Bowen, G.L. (1998). Low Social Support among at-risk adolescents. Social Work in Education, 20(4), 245 – 260.
Roberts, M.C., Brown, K.J., Johnson, R.J., & Reinke, J. (2002). Positive psychology for children: development, prevention, and promotion. In C. R. Snyder & S. Lopez (Eds.), Handbook of positive psychology (pp. 663-675). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Roeser, R. W., Eccles, J. S., & Sameroff, A. J. (2000). School as a context of early adolescents' academic and social-emotional development: A summary of research findings. Elementary School Journal, 100(5), 443-471.
Rolf, J. E., & Johnson, J. L. (1999). Opening doors to resilience intervention for
prevention research. In M. D. Glantz and J. L. Johnson (Eds.), Resiliency and development: Positive life adaptations (pp. 229-249). New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers.
Rosenfeld, L.B., Richman, J.M., Bowen, G.L. (2000). Social support networks and school outcomes: The centrality of the teacher. Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal, 17(3), 205 -226.
Rosenfeld, L.B., Richman, J.M., Bowen, G.L. (1998). Low Social Support among at-risk adolescents. Social Work in Education, 20(4), 245 – 260.
Roth, J., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2002). What is a youth development program? Identification of defining principles. In R. M. Lerner, F. Jacobs & D. Wertlieb (Eds.), Handbook of Applied Developmental Science (Vol. 2, pp. 197-223). Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Roth, J., Brooks-Gunn, J., Murray, L., & Foster, W. (1998). Promoting health adolescents: Synthesis of youth development program evaluations. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 8(4), 423-459.
Rutter, M. (1997). Comorbidity: concepts, claims and choices. Criminal Behavior and Mental Health, 7, 279 - 285.
Rutter, M. (1979). Protective factors in children’s responses to stress and disadvantage. In M.W. Kent and J.E. Rolf (Eds.), Primary prevention of psychopathology: Social competence in children (pp. 49 – 74). Hanover, NH: University Press of New England. Cited in Rosenfeld, L.B., Richman, J.M., Bowen, G.L. (1998). Low Social Support among at-risk adolescents. Social Work in Education, 20(4), 245 – 260.
Ryff, C. D. (1995). Psychological well-being in adult life. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 4, 99-104.
Ryff, C. D. (1989). Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological wellbeing. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 57, 1069 -1081.
Samdal, O., Nutbeam, D., Wold, B., and Kannas, L. (1998). Achieving health and educational goals through schools - a study of the importance of the school climate and the students' satisfaction with school. Health Education Research, 13(3), 383 - 397.
Sameroff, A. J. (2000). Developmental systems and psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 297-312. Scales, P.C., and Leffert, N. (Eds.), (1999). Developmental Assets: A Synthesis of the Scientific Research on Adolescent Development. Search Institute.
Sawyer, M. G., Arney, F., Baghurst, P., Clark, J.J., Graetz, B. W., Kosky, R. J., Nurcombe, B., Patton, G.C., Prior M.R., Raphael, B. Rey, J., Whaites, L.C., and Zubrick, S. R. (2000). The Mental Health of Young People in Australia. Mental Health and Special Programs Branch, Commonwealth Department of Health and Aged Care, Canberra.
Scales, P.C., and Leffert, N. (Eds.), (1999). Developmental Assets: A Synthesis of the Scientific Research on Adolescent Development. Search Institute.
Seals, D. and Young. J. (2003). Bullying and victimization: prevalence and relationship to gender, grade level, ethnicity, self-esteem, and depression. Adolescence, 38(152), 735 - 747.
Search Institute (2003). Developmental Assets Checklist. Personal Communication.
Seligman, M. P. (2002). Positive psychology, positive prevention, and positive therapy. In C. R. Snyder & S. J. Lopez (Eds.), Handbook of positive psychology (pp. 3-9). London: Oxford University Press.
Sennyah, P., Chow, K.H., & Mohamad, S.G. (2000). Mental Act to be amended. In New Strait Times, October 23, 2000.
Schneider, B.H. (1998). Cross-cultural comparison as doorkeeper in research on the social and emotional adjustment of children and adolescents. Developmental Psychology, 34(4), 793 - 797.
Solomon, D., Battistich, V., Watson, M., Schaps, E., and Lewis, C. (2000). A six-district study of educational change: direct and mediated effects of the child development project. School Psychology of Education, 4, 3 - 51.
Steiger, J.H. (1990). Structural model evaluation and modification: an internal estimation approach. Multivariate Behavioural Research, 25, 173 - 180.
Steinberg, L. & Morris, A.S. (2001). Adolescent development. Annual Review of Psychology, 52, 83 - 110.
Stewart, E. A. (2003). School social bonds, school climate, and school misbehavior: A multilevel analysis. Justice Quarterly, 20(3), 575 – 604.
Takakura, M. & Sakihara, S. (2001). Psychological correlates of depressive symptoms among Japanese high school students. Journal of Adolescent Health, 28, 82 – 89.
Tobler, N. S., Roona, M. R., Ochshorn, P., Marshall, D. G., Streke, A. V., & Stackpole, K. M. (2000). School based adolescent drug prevention programs: 1998 meta-analysis. Journal of Primary Prevention, 20, 275-336.
Tucker, L.R. & Lewis, C. (1973). A reliability coefficient for maximum likelihood factor analysis. Psychometrika, 38, 1 - 10.
Tygart, C. (1998). Public school vandalism: Towards a synthesis of theories and transition to paradigm analysis. Adolescence, 23(89), 187 – 200.
Wang M. C., Haertel, G. D., & Walberg,, H. J. (1999). Psychological and Educational Resilience. In A. J. Reynolds, H. J. Walberg, and R. P. Weissberg (Eds.), Promoting positive outcomes: Issues in children’s and families’ lives. Washington, DC: Child Welfare League of America.
Weissberg, R. P., & Greenberg, M. T. (1998). School and community competence-enhancement and prevention programs. In I. E. Sigel & K. A. Renninger (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology (5th ed., Vol. 4: Child psychology in practice, pp. 877-954). New York: Wiley.Welsh, J.A. & Bierman, K.L. (2001). Mastering the social, emotional, and cognitive skills and behaviors needed to succeed as a member of society. Gale Encyclopedia of Childhood and Adolescence. Retrieved on May 27, 2003, from http://www.findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_g2602/is_0004/ai_2602000487
Werner, E.E. (1995). Resilience in Development. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 4(3), 81 – 85.
Werner, E. E. (1993). Risk, resilience, and recovery: Perspectives from the Kauai Longitudinal Study. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 503-515.
Wilkinson, R. B., & Walford, W. A. (1998). The measurement of adolescent psychological health: One or two dimensions? Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 27(4), 443 - 455.
Wilson, D. (2004). The interface of school climate and school connectedness and relationships with aggression and victimization. The Journal of School Health, 74(7), 293 – 299.
World Data on Education (2004). National report on the development of education: Malaysia. Prepared for the International Bureau of Education. Retrieved on May 27, 2004, from http://www.ibe.unesco.org/International/Databanks/Wde/profilee.htm
Yusof, S.A. & Amin, R.M. (1999). Admired values: The case of teenagers in Malaysia. The International Journal of Social Economics, 26(6), 802 -
Zaff, J.F., Smith, D.C., Rogers, M.F., Halle, T.G., & Bornstein, M.H. (2003). Holistic well-being and the developing child. In M.H. Bornstein, L. Davidson, C.L.M. Keyes, & K.A. Moore (Eds.), Well-being: Positive development across the life course. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey.
Zaff, J.F. and Hair, E.C. (2003). Positive development of the self: Self-concept, self-esteem, and identity. In M.H. Bornstein, L. Davidson, C.L.M. Keyes, & K.A. Moore (Eds.), Well-being: Positive development across the life course. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey.